Labs and Tasks: Sum, Product, Counters, Max and Min
Sum (Addition)
Syntax: In Pascal, summation is performed through recursion using the following formula:
S = S + Y
Where:
Sis the cumulative sum;Yis the next addend.
Labs and Tasks
Sum (Additions)
Lab 1:
To do: 10 numbers are given. It’s necessary to compute their sum.
✍Algorithm:

The variable sum is initialized to 0 before the loop begins. During every iteration, the variable sum increases by the current number's value.
{0.3 points} Task 1, sum:
To do: Enter 5 integers. After each entry, the program should print their running sum.
Expected output:
'please, enter 5 numbers:'
>>> 4
entered number: 4 => sum = 4
>>> 7
entered number: 7 => sum = 11
>>> 3
entered number: 3 => sum = 14
... etc.
[Program name: task-01-sum.pas]
{0.3 points} Task 2, sum:
To do: Enter 5 real numbers. The program outputs their sum only once, right before exiting.
Expected output:
entered numbers:
>>> 4.2 >>> 7.1 >>> 3.1 >>> 2.5 >>> 8.6
sum = 25.5
[Program name: task-02-sum.pas]
{0.3 points} Task 3, sum:
To do: Compute the sum of 10 consecutive numbers: 1 + 2 + 3 + … + 10. It's recommended to use a for loop.
[Program name: task-03-sum.pas]
{0.3 points} Task 4, sum:
To do: Compute the sum of five odd numbers: 1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 9. Use a for loop with an arbitrary step.
Expected output:
'1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 9 ='
25
[Program name: task-04-sum.pas]
{0.4 points} Task 5, sum:
To do: Calculate the sum of all odd integers up to 99 (i.e., 1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 9 + 11 + … + 99). Use a for loop with an arbitrary step.
Expected output:
'1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 9 + ... + 99 ='
2500
[Program name: task-05-sum.pas]
{0.4 points} Task 6, sum:
To do: Calculate the sum of all odd integers up to 99 (i.e., 1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 9 + 11 + … + 97 + 99). Use a regular loop.
[Program name: task-06-sum.pas]
To do: 10 integers are given. Calculate their sum.
✍Algorithm:

{0.3 points} Task 7, sum:
To do: 5 integers are entered. The program should output their sum only once, before the end of the program. Use the same format as shown in the lab.
[Program name: task-07-sum.pas]
Product (Multiplication)
Lab 3:
To do: 10 real numbers are given. Calculate their product (multiplication).
✍Algorithm:

The variable product is initialized with the value 1 before the loop starts. Each loop iteration multiplies the current value of product by the next number.
{0.3 points} Task 1, product:
To do: 5 integers are entered. After each entry, the program prints their product.
Expected output:
'please, enter 5 numbers:'
>>> 4
entered number: 4 => product = 4
>>> 3
entered number: 3 => product = 12
>>> 5
entered number: 5 => product = 60
[Program name: task-01-product.pas]
{0.3 points} Task 2, product:
To do: 5 real numbers are entered. The program outputs their product only once, immediately before ending execution.
Expected output:
entered numbers:
>>> 4.2 >>> 7.1 >>> 3.1 >>> 2.5 >>> 8.6
product = 1987.503
[Program name: task-02-product.pas]
{0.4 points} Task 3, product:
To do: Calculate the product of 2-digit even integers within the interval [10;30]: 10 × 12 × 14 × … × 28 × 30. Use a for loop with an arbitrary step.
Expected output:
product = 165412864
[Program name: task-03-product.pas]
Lab 4: Product (Multiplication) – Short Solution
To do: 10 real numbers are given. Calculate their product.
✍Algorithm:

{0.1 points} Task 4, product:
To do: 5 real numbers are entered. The program outputs their product only once, immediately before ending execution.
Expected output:
entered numbers:
>>> 4.2 >>> 7.1 >>> 3.1 >>> 2.5 >>> 8.6
product = 1987.503
[Program name: task-04-product.pas]
{0.3 points} Task 5, product:
To do: 5 integers are entered. The program outputs their product only once, immediately before ending execution. Use the concise format demonstrated earlier.
Expected output:
enter 5 integers, please:
>>>2 >>>5 >>>1 >>>7 >>>3
product is: 210
[Program name: task-05-product.pas]
Counters
Lab:
To do: Given n ≥ 0, the program asks to input n integer numbers and finds the quantity of odd numbers among those entered.
Solution: We'll utilize an if statement inside a loop.
Expected output:
how many numbers?
>>>4
enter the numbers:
>>>1 >>>3 >>>8 >>>7
the number of odd: 3
✍ Algorithm:
Counters
{0.2 points} Task 1, counters:
To do: Output a sequence: 1 2 3 4 . . . 99 100. Use a loop and a variable named counter.
Code snippet:
...
var counter:=0;
loop 100 do
begin
...
print(counter);
end;
Expected output:
1 2 3 4 5 . . . 99 100
[Program name: task-01-counters.pas]
{0.3 points} Task 2, counters:
To do: Output a sequence: 1 2 3 4 . . . 99 100 99 . . . 3 2 1.
Note: Create two loops: the first one iterates through 1 2 3 4 . . . 99 100, the second one through 99 . . . 3 2 1.
Expected output:
1 2 3 4 . . . 97 98 99 100 99 98 . . . 4 3 2 1
[Program name: task-02-counters.pas]
{0.2 points} Task 3, counters:
To do: Ten randomly generated integers are provided. Your goal is to determine the number of positive integers using a for loop and a variable called counter.
Note: Utilize the random function to generate a series of random numbers:
var genNumb: integer;
//...
genNumb:=random (-5, 10);
You may finish the following code:
begin
var genNumb, i: integer;
var counter := 0;
for i := 1 to 10 do
begin
genNumb := random(-5, 10);
// to do ...
// ...
end;
writeln;
print('numbers of positive: ', counter)
end.
Expected output:
1 6 10 10 -2 1 -4 4 -4 2
numbers of positive: 7
[Program name: task-03-counters.pas]
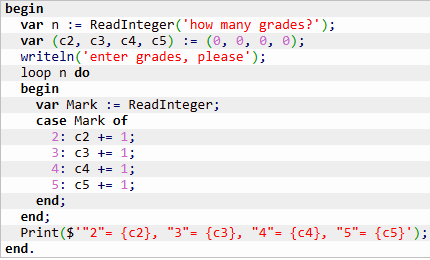
Several Counters
Lab:
To do: A pupil received n exam marks (grades ranging from 2 to 5). Calculate the number of occurrences for each mark ("2"s, "3"s, etc.).
Solution: We'll use multiple counters, one for each grade.
Expected results:
how many grades? 5
enter grades, please
4
4
4
2
3
"2"= 1, "3"= 1, "4"= 3, "5"= 0
✍ Algorithm:
Counters
{0.4 points} Task 4, counters:
To do: Generate 10 random integers. Use a loop and two counters to find the quantities of positive and negative numbers.
Note: Use the random function to produce a random sequence of numbers:
var genNumb: integer;
//...
genNumb:=random (a,b);
Expected output:
1 -5 -12 2 3 9 -1 9 5 -8
counter positive = 6, counter negative = 4
[Program name: task-04-counters.pas]
{0.4 points} Task 5, counters:
To do: Generate 10 random integers. Use a loop and two counters to find the quantities of even and odd numbers.
Expected output:
1 -5 -12 2 3 9 -1 9 5 -8
counter even = 3, counter odd = 7
[Program name: task-05-counters.pas]
Minimum and Maximum Value
Lab:
To do: Given n numbers (n ≥ 0), find the minimum value among them.
✍Algorithm:
Solution 1: Assign the first entered number to the variable min. Then, during the loop, compare subsequent numbers with min. If any number is smaller, update min accordingly.
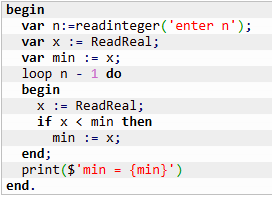
What is not good: The first value is handled separately.
Solution 2: Set the initial value of min variable to the maximum possible value of real type (real.MaxValue). Then, in the loop, check if the currently entered number is less than min. If it's true, update min with the new value.
The idea: After the first iteration, min will definitely be updated since any actual number is guaranteed to be smaller than real.MaxValue.
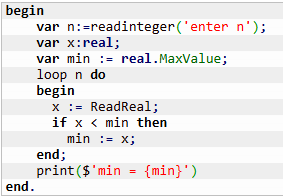
Min & Max Problems
{0.2 points} Task 1, min & max:
To do: Input 5 numbers. Output the maximum and minimum of the entered numbers.
Note: Complete the following code snippet:
begin
var // ...;
var min := integer.MaxValue;
var max := integer.MinValue;
loop 5 do
begin
// ...
end;
print($'min = {min}, max = {max}')
end.
Expected output:
enter 5 integers:
>>> 5 >>> 3 >>> 8 >>> 1 >>> 2
maximum is 8, minimum is 1
[Program name: task-01-maxmin.pas]
{0.5 points} Task 2, min & max:
To do: An integer N is given, representing the number of rectangles. Each rectangle is described by its side lengths a and b. Calculate the areas of all rectangles (S = a * b) and output the minimum area.
Expected output:
How many rectangles?
>>> 3
Please, enter the sides of the rectangles:
>>> 2 >>> 3
area is: 6
>>> 1 >>> 5
area is: 5
>>> 4 >>> 2
area is: 8
The minimum area of all rectangles is 5
[Program name: task-02-maxmin.pas]
{0.5 points} Task 3, min & max:
To do: An integer N is given, representing the number of rectangles. Each rectangle is described by its side lengths a and b. Calculate the perimeters of all rectangles and output the maximum perimeter.
Expected output:
How many rectangles?
>>> 3
Please, enter the sides of the rectangles:
>>> 2 >>> 3
perimeter: 10
>>> 1 >>> 5
perimeter: 12
>>> 4 >>> 2
perimeter: 12
The maximum perimeter of all rectangles is 12
[Program name: task-03-maxmin.pas]
{0.3 points} Task 4, min & max:
To do: Find the minimum of 5 numbers and output its sequential number (position/order number). Store the sequential number using an additional variable.
Note: Use the random function to create a randomized sequence of numbers:
var genNumb: integer;
//...
genNumb:=random (a,b);
Expected output:
5 generated numbers:
5 3 8 1 2
minimum is 1, its position is 4
[Program name: task-04-maxmin.pas]
{0.5 points} Task 5, min & max:
To do: Calculate the minimum and maximum of 10 generated numbers and print the sum of their sequential numbers (positions or serial numbers).
Note: Use the random function to create a randomized sequence of numbers:
var genNumb: integer;
//...
genNumb:=random (a,b);
Expected output:
10 generated numbers:
2 15 3 8 1 2 9 1 7 11
max is 15 position is 2, min is 1 position is 8, 2 + 8 = 10
[Program name: task-05-maxmin.pas]
Sums and Products in While and Repeat Loops
Lab:
To do: Calculate the sum of the arithmetic progression: 11 + 13 + 15 + ... + 99.
Expected results:
sum = 2475
✍ Algorithm:
While loop:
Loop:
Sums and While Loops
{0.3 points} Task 1, sum and while:
To do: Calculate the sum of all odd 2-digit integers (11 + 13 + 15 + 17 + 19 + 21 + ... + 99). Solve the problem twice: using while and repeat loops.
Expected output:
while loop. sum = 2475
repeat loop. sum = 2475
[Program name: task-01-sum-while.pas]
{0.3 points} Task 2, sum and while:
To do: Calculate the product of 2-digit even integers in the range [10;30] (10 × 12 × 14 × ... × 28 × 30). Solve the problem twice: using while and repeat loops.
Expected output:
while loop. product = 667418624
repeat loop. product = 667418624
[Program name: task-02-sum-while.pas]
{0.3 points} Task 3, sum and while:
To do: Enter 5 real numbers. The program should output their sum only once, just before the end of the program. Solve the problem twice: using while and repeat loops.
Expected output:
please enter 5 numbers:
>>> 4.2 >>> 7.1 >>> 3.1 >>> 2.5 >>> 8.6
sum = 25.5
[Program name: task-03-sum-while.pas]
{0.3 points} Task 4, sum and while:
To do: Enter 5 numbers. The program should output their product (multiplication) only once, just before the end of the program. Solve the problem twice: using while and repeat loops.
Expected output:
please enter 5 numbers:
>>> 4 >>> 7 >>> 3 >>> 2 >>> 8
multiplication = 1344
[Program name: task-04-sum-while.pas]