Labs and Tasks: Nested Loops, Infinite loops, Break operator
Nested Loops
Lab 1:
To do: Calculate the value of the function z(x,y) = xy for every x changing in the interval [2;8], and y changing in the interval [2;4].
Expected output:
z(x,y) = 2^2 = 4
z(x,y) = 2^3 = 8
z(x,y) = 2^4 = 16
z(x,y) = 3^2 = 9
z(x,y) = 3^3 = 27
z(x,y) = 3^4 = 81
z(x,y) = 4^2 = 16
z(x,y) = 4^3 = 64
z(x,y) = 4^4 = 256
z(x,y) = 5^2 = 25
z(x,y) = 5^3 = 125
z(x,y) = 5^4 = 625
... etc.
✍Algorithm:
We must create two nested for loops: one loop within another. The outer loop modifies variable x, while the inner loop changes variable y.
{0.4 points} Task 1, nested loops:
To do: Calculate the function z(x,y) = x + 2*y for every x varying in the interval [5;10] and y varying in the interval [1;5]. Use nested for loops.
[Program name: task-01-nested_loops.pas]
Expected output:
z(x,y)= 5+2*1 = 7
z(x,y)= 5+2*2 = 9
z(x,y)= 5+2*3 = 11
z(x,y)= 5+2*4 = 13
z(x,y)= 5+2*5 = 15
z(x,y)= 6+2*1 = 8
z(x,y)= 6+2*2 = 10
z(x,y)= 6+2*3 = 12
z(x,y)= 6+2*4 = 14
z(x,y)= 6+2*5 = 16
z(x,y)= 7+2*1 = 9
z(x,y)= 7+2*2 = 11
z(x,y)= 7+2*3 = 13
z(x,y)= 7+2*4 = 15
z(x,y)= 7+2*5 = 17
z(x,y)= 8+2*1 = 10
z(x,y)= 8+2*2 = 12
z(x,y)= 8+2*3 = 14
z(x,y)= 8+2*4 = 16
z(x,y)= 8+2*5 = 18
z(x,y)= 9+2*1 = 11
z(x,y)= 9+2*2 = 13
z(x,y)= 9+2*3 = 15
z(x,y)= 9+2*4 = 17
z(x,y)= 9+2*5 = 19
z(x,y)= 10+2*1 = 12
z(x,y)= 10+2*2 = 14
z(x,y)= 10+2*3 = 16
z(x,y)= 10+2*4 = 18
z(x,y)= 10+2*5 = 20
{0.4 points} Task 2, nested loops:
To do: Calculate the function z(x,y) = x - y for every x varying in the interval [30;33] and y varying in the interval [1;5]. Use nested for loops.
Expected output:
30-1=29
30-2=28
30-3=27
30-4=26
30-5=25
31-1=30
31-2=29
31-3=28
31-4=27
31-5=26
32-1=31
32-2=30
32-3=29
32-4=28
32-5=27
33-1=32
33-2=31
33-3=30
33-4=29
33-5=28
[Program name: task-02-nested_loops.pas]
{0.4 points} Task 3_0, nested loops:
To do: Display rows with the specified pattern of repeating numbers as follows. Use nested loops: the outer loop iterates over rows, the inner loop handles the repetition of numbers within each row.
Expected output:
9 9 9 9 9
8 8 8 8 8
7 7 7 7 7
6 6 6 6 6
5 5 5 5 5
[Program name: task-3_0-nested_loops.pas]
{0.4 points} Task 3_1, nested loops:
To do: Display rows with the specified pattern of repeating numbers as follows. Use nested loops: the outer loop iterates over rows, the inner loop handles the repetition of numbers within each row.
Expected output:
0 0 0 0 0
1 1 1 1 1
2 2 2 2 2
3 3 3 3 3
4 4 4 4 4
5 5 5 5 5
6 6 6 6 6
7 7 7 7 7
8 8 8 8 8
9 9 9 9 9
[Program name: task-3_1-nested_loops.pas]
{0.4 points} Task 4, nested loops:
To do: Display rows with the specified pattern of repeating numbers as follows. Use nested loops and arbitrary step equal to 2.
Expected output:
1 1 1 1 1 1
3 3 3 3 3 3
5 5 5 5 5 5
7 7 7 7 7 7
9 9 9 9 9 9
[Program name: task-04-nested_loops.pas]
{0.7 points} Task 5, nested loops:
To do: Given integers K > 0 and N ≥ 0. There are K sequences of integers, each containing N elements. The program needs to output the number of odd elements in each sequence.
Note: It is advisable to use the random function to generate the sequences. However, don't forget to print the elements of each sequence.
Expected output:
please, enter the quantity of the sequences:
>>> 3
enter the quantity of numbers within the sequences
>>> 5
the sequence #1
4 9 3 3 7 result: 4 odd elements
the sequence #2
6 9 8 2 9 result: 2 odd elements
the sequence #3
5 1 7 3 6 result: 4 odd elements
[Program name: task-05-nested_loops.pas]
{0.7 points} Task 6, nested loops:
To do: Given integers K > 0 and N ≥ 0. There are K sequences of integers, each containing N elements. The program needs to output the minimum and maximum element in each sequence.
Note 1: It is advisable to use the random function to generate the sequences. However, don't forget to print the elements of each sequence.
Note 2: Preferably initialize the minimum and maximum variables with appropriate constants:
min:=integer.MaxValue;
max:=integer.MinValue;
Expected output:
please, enter the quantity of the sequences:
>>>3
enter the quantity of numbers within the sequences
>>>5
the sequence #1
4 9 5 4 8 min =4, max=9
the sequence #2
6 9 2 3 4 min =2, max=9
the sequence #3
9 1 4 8 7 min =1, max=9
[Program name: task-06-nested_loops.pas]
Boolean Type (Logical)
Lab 3, boolean type:
To do: Values of n and k are given. n numbers are entered. The program should output whether the number k exists among them (output must be of Boolean type).
Expected output:
how many numbers (n)?
>>>5
what number must we find (k)?
>>>3
enter numbers, please
>>>1 >>>3 >>>6 >>>4 >>>7
there is '3' number: True
✍Algorithm:

Break and Continue
Lab 4, break:
To do: The values of n and k are entered. Next, n numbers of the sequence are entered. The program checks if the number k appears in the sequence.
✍Algorithm:
{0.4 points} Task 7, boolean type:
To do: Integers K > 0 and N ≥ 0 are given. There are K sequences of integers, each consisting of N elements. The program should output whether the number 2 appears in any of the sequences and also report the total occurrence of the number 2.
Expected output:
please, enter the quantity of the sequences:
>>> 3
enter the quantity of numbers within the sequences:
>>> 2
input the sequence #1:
>>> 1 >>> 5
input the sequence #2:
>>> 2 >>> 5
input the sequence #3:
>>> 5 >>> 7
there is a number '2': true
total quantity of '2': 1
[Program name: task-07-bool.pas]
Infinite Loops
Examples:
-
while true do begin ... end; end. -
repeat ... until false; -
var x:=1; while x>0 do begin ... end; end. -
var x:=1; repeat ... until x<=0; end.
Lab 5, infinite loops:
To do: A sequence of integers is given. The final number of the sequence is 0 (when 0 is entered, the input stops). The program counts and outputs the number of positive elements in the sequence.
Expected output:
please, enter the sequence, print 0 if you want to stop:
>>>1 >>>-5 >>>9 >>>5 >>>0
positive: 3
please, enter the sequence, print 0 if you want to stop:
>>>1 >>>-2 >>>-5 >>>-9 >>>11 >>>0
positive: 2
✍Algorithm:
Solution 1:
Solution 2:
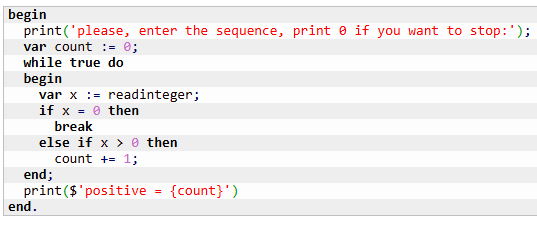
Infinite Loops
{0.4 points} Task 8, infinite loops:
To do: A sequence of integers is given. The last number of the sequence is 0 (when 0 is entered, the input stops). The program calculates and outputs the minimum and maximum values of the sequence. Use an infinite loop.
Expected output:
please, enter the sequence, print 0 if you want to stop:
>>>1 >>>-2 >>>-5 >>>-9 >>>11 >>>0
min = -9 max = 11
[Program name: task-08-infinite_loops.pas]
{0.7 points} Task 9, infinite loops:
To do: An integer K > 0 is given, representing the number of sequences. The last number of each sequence is 0 (when 0 is entered, the input stops). The program outputs the number of elements in each sequence and the total number of elements across all sequences.
Expected output:
please, enter the quantity of the sequences
>>> 3
input the sequence #1
>>>1 >>>5 >>>8 >>>0
the seq has 3 elements
input the sequence #2
>>>7 >>>2 >>>0
the seq has 2 elements
input the sequence #3
>>>6 >>>0
the seq has 1 elements
Total number of elements: 6
[Program name: task-09-infinite_loops.pas]
Working with Digits of Natural Numbers
Lab 6:
To do: A natural number m is given. Calculate the sum of its digits.
Solution: Use div and mod operations to extract individual digits from the number.
Expected output:
m:
>>> 425
result: 11
✍Algorithm:
{0.7 points} Task 10, digits:
To do: An integer (variable a) is given. Find the number of its digits and their product.
Note: Since the entered number could be negative, use the abs function to obtain the absolute value of the number:
abs(m)
Expected output:
N:
>>> 1205
Count = 4, product = 0
--
N:
>>> -111
Count = 3, product = -1
[Program name: task-10-loops.pas]
{0.7 points} Task 11, digits:
To do: A natural number m is given. Determine how many even digits appear in its decimal representation.
Expected output:
m:
>>> 745
even: 1
[Program name: task-11-loops.pas]
Sequences in While Loops
Lab 7, sequences:
To do: A sequence of integers is given. The last number of the sequence is 0 (when 0 is entered, the input stops). The program determines if the sequence is non-increasing (i.e., each successive number is less than or equal to the previous one). If yes, output 0; otherwise, output 1.
Expected output:
please, enter the sequence, print 0 if you want to stop:
>>>1 >>>5 >>>9 >>>5 >>>0
output: 0 (non-increasing sequence)
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
please, enter the sequence, print 0 if you want to stop:
>>>1 >>>2 >>>5 >>>9 >>>11 >>>0
output: 1 (increasing sequence)
✍Algorithm:
Solution 1:
Solution 2:
{0.7 points} (Complex) Task 12, loops:
To do: An integer K > 0 is given, representing the number of sequences. The last number of each sequence is 0 (when 0 is entered, the input stops). The program checks if there is at least one element in each sequence that is smaller than its immediate predecessor. If such an element exists, output true; otherwise, output false.
Expected output:
'please, enter the quantity of the sequences:' 3
'input the sequence #1:'
1 5 3 0
>>> output: true
'input the sequence #2:'
2 6 0
>>> output: false
'input the sequence #3:'
5 7 4 0
>>> output: true
[Program name: task-12-loops.pas]
{1.0 points} (Complex) Task 13, loops:
To do: A sequence is called "sawtoothed" if each element is either larger or smaller than both of its neighboring elements. Given a sequence of integers (with at least two elements), the last number being 0 (indicating termination), check if the sequence is sawtoothed. Output True or False.
Note 1: A sequence of two elements is automatically considered sawtoothed if the elements differ.
Note 2: To track whether the sequence is sawtoothed, use a variable of Boolean type:
var flag := true;
Note 3: No need to explicitly check that the sequence contains at least two elements.
Expected output:
enter the sequence:
>>> 2 >>> 9 >>> 1 >>> 7 >>> 5 >>> 0
sawtoothed: True
---
enter the sequence:
>>> 1 >>> 2 >>> 3 >>> 2 >>> 5 >>> 0
sawtoothed: False
[Program name: task-13-loops.pas]
{0.4 points} Task 14:
To do: An integer N is given, followed by a set of N numbers. Find the index (serial number) of the first minimal element and the index of the last maximal element.
Expected output:
enter 10 numbers:
>>>2 >>>15 >>>3 >>>8 >>>1 >>>2 >>>9 >>>1 >>>15 >>>11
serial numb of min is 5, serial numb of max is 9
[Program name: task-14.pas]
{0.3 points} Task 15, loops:
To do: An integer n is entered. Print the first n terms of the Fibonacci sequence.
Expected output:
enter n:
>>> 8
result: 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21
[Program name: task-15-fib.pas]