Lesson #6. Chained IF statements and Case statement. String type
Chained IF statements
Example:
Given: a sequence number of a Season (Winter is first)
Output: Name of Season

✎
1. {0.5 points}[task-01-ch-if.pas] Make the next task using Chained If statement: Student has got a mark. If it is 2 mark then the program has to output "it's very bad"; if it is 3 - program has to output "it's bad"; if it is 4 - "it's good", in the case of 5 - "it's excellent", otherwise - "such marks do not exist" .
2 >>> "it's very bad" 4 >>> "it's good"
2. {0.5 points}[task-02-ch-if.pas]Make the next task using Chained If statement: The program must request the time of a day in hours (from 1 up to 24). Depending on the time entered, display a message indicating what time of day the entered hour belongs to (midnight (24), night (1-4), morning (5-11), day (12-16), evening (17-23)).
Example:
2 >>> "night" 24 >>> "midnight"
Case statement
We use case statement in a situation of multiple choice.
Given: a sequence number of a Season (Winter is first)
Output: Name of Season
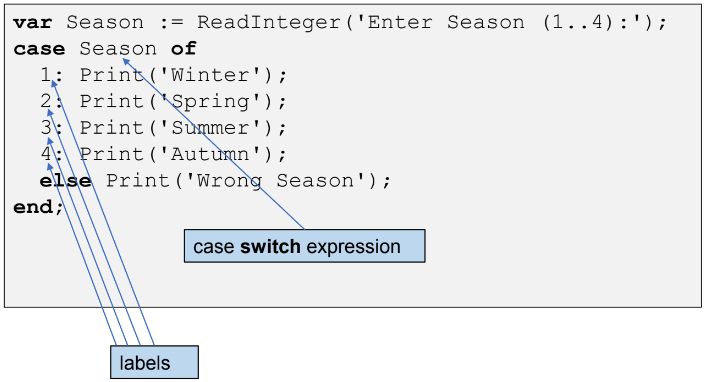
✎
1. {0.5 points}[task-01-case.pas] Make the next task using Case statement: Student has got a mark. If it is 2 mark then the program has to output "it's very bad"; if it is 3 - program has to output "it's bad"; if it is 4 - "it's good", in the case of 5 - "it's excellent", otherwise - "such marks do not exist" .
2. {0.5 points}[task-02-case.pas]Make the next task using Case statement: An integer in the range 1–7 is given. Output a name of the day corresponding to this number (1 - “Monday”, 2 - “Tuesday”, etc.).
Example:
1 >>> Monday 7 >>> Sunday
3. {0.5 points}[task-03-case.pas]Make the next task using Case statement:
Arithmetic operations are numbered as follows: 1 - addition, 2 - subtraction, 3 - multiplication, 4 - division. Ask user to enter number - arithmetic operation (integer in the range 1–4) and two reals A and B (B is not = 0). Output the result of the specified arithmetic operation with the given numbers.
Example:
'Enter arithmetic operation, please (from 1 till 4):' 1 'Enter two real numbers:' 2.2 5.0 >>> the result is 2.2+5.0=7.2 ... 'Enter arithmetic operation, please (from 1 till 4):' 2 'Enter two real numbers:' 5.3 3.2 >>> the result is 5.3-3.2=2.5
4. {0.5 points}[task-04-case.pas]Make the next task using Case statement: Program requests the number of the mass units (1 means kilogram, 2 means ounce, 3 - gram, 4 - ton, 5 - pound). Then the program requests body weight in one of these units. Output body weight in kilograms (1 ounce = 0.0283 kilograms, 1 gram = 0.0010 kilograms, 1 ton = 1000 kilograms, 1 pound = 0.4536 kilograms).
Example:
'enter mass unit, please: ' 1 'enter body weight, please: ' 3 >>> result: 3 kilograms = 3 kilograms ... 'enter mass unit, please: ' 3 'enter body weight, please: ' 4 >>> result: 4 grams = 0.004 kilograms ... 'enter mass unit, please: ' 4 'enter body weight, please: ' 4 3 4 >>> result: 4 tons = 4000 kilograms
Using String type
The variable in case statement may be of String type.
Given: the english words 'dog', 'use', 'find'
Output: translations of the words into russian
✎
5. {0.5 points}[task-05-case.pas]Make the next task using Case statement: The program must request the time of a day midnight or night or morning or day or evening. The program has to display a range of hours belonging to entered time of a day (midnight (24), night (1-4), morning (5-11), day (12-16), evening (17-23)).
Example:
'Enter a time of a day, please: ' morning >>> result: a range of hours for morning is 5-11 ... 'Enter a time of a day, please: ' evening >>> result: a range of hours for evening is 17-13
Using ranges and enumerations
Given: A sequence number of a Month
Output: Calculate a name of a season
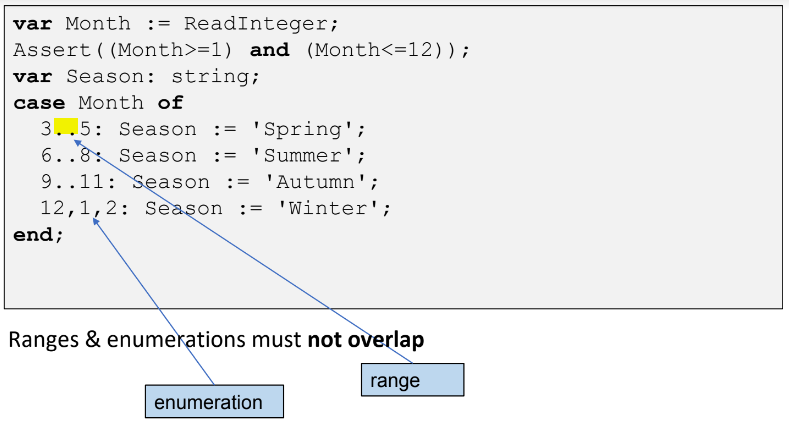
✎
6. {0.5 points}[task-06-case.pas]Make the next task using Case statement: The program must request the time of a day in hours (from 1 up to 24). Depending on the time entered, display a message indicating what time of a day the entered hour belongs to (midnight (24), night (1-4), morning (5-11), day (12-16), evening (17-23)).
Example:
'Enter a time of a day in hours (from 1 till 24), please: ' 14 >>> result: 14 hours belongs to day ... 'Enter a time of a day in hours (from 1 till 24), please: ' 24 >>> result: 24 hours belongs to midnight
7. {0.5 points}[task-07-case.pas] Make the next task using Case statement: The program must request number - the age. Depending on the entered number display a message indicating the age of person in words (infancy: from 0 to 1 year old, early childhood: 2-4 years old, preschool: 5-7 years old, school age: 8 - 12 years old, youth: 13-19 years old, second youth: 20–35 years old, adulthood: 36-65 years, old age: from 66 years).
Example:
'enter the age, please:' 6 >>> preschool ... 'enter the age, please:' 37 >>> adulthood
Extra tasks (Test)
1. {0.5 points}[task-1-extra-if-case.pas] The integers x and y are given. Calculate the value of the function:
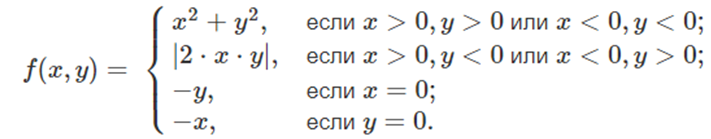
2. {0.5 points}[task-2-extra-if-case.pas] The commands are numbered as follows:
2 — check if the number is odd;
3 — check if the number is the divisible by the specified number
D (the number D is entered by the user when this command is selected).
You must ask the user to input an integer N - the sequence number of the C command, and then to output the result. For example, for the command "2" output True if the number is odd and False otherwise.
Note. In response to entering an incorrect command, you should display the message "Command is unknown!".
Examples:
N = -23, C = 1 >>> True
N = 103, C = 3, D = 7 >>> False
N = 12, C = 1 >>> False
N = 245, C = 2 >>> True
3. {0.5 points}[task-3-extra-if-case.pas] An integer N is given, |N| ∈ 10..99.
‒ If it is even and is divided by 4, then "add" digit 4 to the left of the number (that is, to form a new number, which in the category of hundreds has 4, and the digits of tens and units are left as in the original number);
‒ if even, but is not divided by 4, then add digit 2 to the left of the number;
‒ if odd, then "add" digit 0 to the right of the number. Print the resulting number.
Examples:
N = 16 >>> N = 416
N = 86 >>> N = 286
N = 31 >>> N = 310
4. {0.5 points}[task-4-extra-if-case.pas] The locator is oriented to one side of the world:
"N" — North,
"W" — West,
"S" — South,
"E" — East) And the locator also can take three digital turn commands:
1 — turn right,
-1 — turn left,
2 — turn 180°.
The symbol C is given— the initial orientation of the locator, and integers N1 and N2 — they are two sent commands. Calculate the orientation of the locator after executing these commands and display it.
Note.
If incorrect initial orientation of the locator was input it is necessary to output the message "Incorrect input!" and terminate the program (exit statement). Entering an incorrect command does not process.
Example of using the exit statement:
begin
var n := ReadlnInteger('please, enter positive N: ');
if n <= 0 then
begin
Writeln('incorrect input!');
exit;
end;
// the next code
end.
Comment.
The most effective solution to this problem is only twocase operators (they are not nested).