Lesson #14. Functions
- Function is a kind of procedure that returns a value to the main program to use it in an expression:
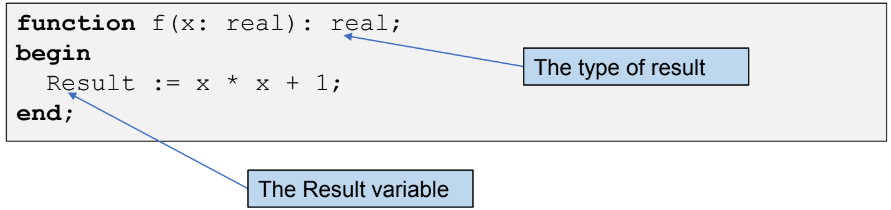
Function definition
Function definition differs from procedure definition by two positions:- We have to write the Type of the value that function returns.
- We have to use Result variable to store the result of the function.
begin
println(f(2)); // 5
end.
********************************************************************************************* Example 1:
Body of function can have loops:
Task: Calculate the factorial of the number, using the function. Call the function with a parameter equals to value of 5 (calculate 5!).
Solution:
begin
println ('5! = ', Fact(5)) // 5! = 120
end.
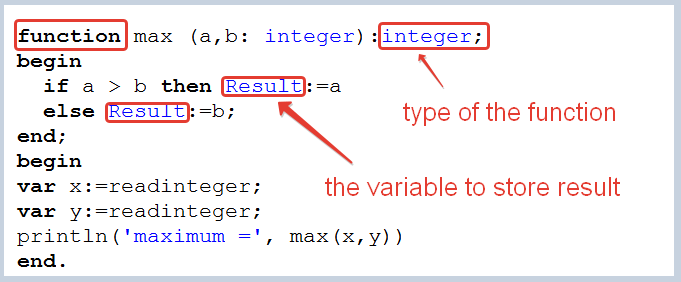
Example 2:
Task: Find the maximum among two numbers using the function.
Solution:
******************************************************************************
✎
1.{0.3 points}[L14-task01.pas] Find the minimum among three numbers using the function (with three parametrs).
Example:
'please, input three numbers' 2 5 9 minimum = 2
2.{0.3 points}[L14-task02.pas] Find the sum (addition) of two entered numbers using the function (with two parametrs).
Example:
'please, input two numbers' 2 5 sum = 7
3.{0.3 points}[L14-task03.pas] Find the average value (the arithmetic mean) of three entered numbers using the function (with three parametrs).
Example:
'please, input three numbers' 2 5 2 average = 3
4.{0.5 points}[L14-task04.pas] Define the IsDigit(D) function, which returns true if the integer D is a digit (that is D is in the range [0,9]). In the main program output the value of this function for entered number N.
Example:
'please, input number' 42 false ************************* 'please, input number' 4 true
Short function definition
If the result of the function is only one statement, we can use the short function definition:

Example:
Task: Find the hypothenuse of the triangle using the function.
Solution:
*******************************************************************************
✎
5.{0.6 points}[L14-task05.pas] Define the CircleS(R) function of real type that returns the area of a circle with radius R (R is entered real). Use this function to find the area of three circles with these radii. The area of a circle of radius R is calculated by the formula S=π*R2. As the value of PI (π), use 3.14.
6.{0.5 points}[L14-task06.pas] Define the Triangle(a, h) function that finds the perimeter of an isosceles triangle by its base a and the height h drawn to the base (a and h are real). By calling this function find the perimeters of the three triangles for which the bases and heights are given (perimeter = sum of the lengths of all the sides). To find the side b of a triangle, use the Pythagorean theorem: b2=(a/2)2+h2.
Functions as Algorithm Wrappers
We can "wrap" our previous algorithms by functions. For this purpose we must define function parameters, their types and the type of a value the function returns.
Example 1:
*******************************************************************************
✎
7. {0.5 points}[L14-task07.pas] A two-digit integer is entered. Output its right and left digits séparated by commas. Use the functions.
example:
-35 >>> 5, 3 90 >>> 0, 9
8 {0.5 points}[L14-task08.pas] A three-digit integer is entered. Output all of its digits (the order does not matter). Check the correctness of your program, give the log in the form of a comment. Use the functions.
-105 >>> 5, 0, 1 +++++++++++++++++ -105 >>> 1, 0, 5
9. {0.7 points}[task-09.pas] A three-digit integer is entered. Output the addition of its digits. Use the functions.
10. {0.7 points}[task-10.pas] Two digits from 0 up to 9 are given. Use the standard form of a number to make a number the digits of which are the specified digits. Use the functions.
3, 5 >>> 35 7, 0 >>> 70 0, 4 >>> 4**************************************************************
Example 2:
Task: Find the maximum and Minimum among 2 numbers. Use a function. Type of the function is tuple.
Solution:
✎
11. {0.5 points}[task-11.pas] Find middle value among 3 numbers. Use a function.
3, 5, 1 >>> 5 7, 0, 6 >>> 6 4, 1, 5 >>> 4
12. {0.5 points}[task-12.pas] Find the maximum and Minimum among 3 numbers. Use a function. Type of the function is tuple (min and max).
3, 5, 1 >>> 1, 5 7, 0, 6 >>> 0, 7 4, 1, 5 >>> 1, 5********************************************************
Example 3:
Sometimes functions return string value.
Task: Output the season by it's sequence number .
Solution:
****************************************************************************
✎
13. {0.5 points}[L14-task13.pas] Output the day of the week by it's sequence number .
3 >>> Tuesday +++++++++++++++++ 1 >>> Sunday
*********************************************************************************
Example 4:
Task: Output the sum (addition) of n entered numbers.
Solution:
*********************************************************************************
✎
14. {0.3 points}[L14-task14.pas] Output the product (multiplication) of n entered numbers.
'How many numbers?' 3 2 4 3 >>> 24
15. {0.5 points}[L14-task15.pas] Output the quantity of positive numbers among n entered numbers.
'How many numbers?' 5 2 4 -3 5 -4 >>> 3 positive numbers
16. {0.5 points}[L14-task16.pas] Output the quantity of even numbers among n entered numbers.
'How many numbers?' 5 2 4 3 5 4 >>> 3 even numbers
17. {0.6 points}[L14-task17.pas] Output the sum of the sequence: 1 2 3 4 ... n (n is entered and is a parameter of the function).
'n - ?' 5 >>> 15 // (1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5)
*********************************************************************************
Example 5:
Task: Calculate the sum (addition) of the digits of the entered number.
Solution:
*********************************************************************************
✎
18. {0.6 points}[L14-task18.pas] Output the product (multiplication) of the digits of the entered number.
'Please, input the number:' 35 >>> 15
*********************************************************************************
Example 6:
Function can return the value of boolean type:Task: Output true if the entered number is prime and output false otherwise. Use a function.
Solution:
19. {0.6 points}[L14-task19.pas] Describe the IsDigit(A) function, which returns true if entered integer A represents a digit (that is A is in the range [0,9]). In the main program call this function for 4 given numbers (the function call has to be in a loop).
'Please, input the number:' 35 >>> false 'Please, input the number:' 3 >>> true 'Please, input the number:' 9 >>> true 'Please, input the number:' 10 >>> false
Local and global variables
*************************************************************************
Generic procedures and functions
The procedure or function is called generic if it is defined for an arbitrary data type.
The generic subprogram type inference in compile-time is called instantiation.
*********************************************************************************
✎
20. {0.6 points}[L14-task20.pas] Describe a generic function Amean (X, Y), which calculates the arithmetic mean of X and Y.
{0.6 points}[L14-task21.pas] Describe in a short form generic function Amean (X, Y), which calculates the arithmetic mean of X and Y.
22. {0.6 points}[L14-task22.pas] Describe in a short form generic function Gmean (X, Y), which calculates the geometric mean of X and Y.
*********************************************************************************